A lot of investors do not necessarily target racy returns from high-risk growth shares. Instead they may be looking for relatively stable returns from mature businesses with resilient customer demand. I think that helps explain the appeal for some people of National Grid (LSE: NG) shares. The National Grid dividend yield is a juicy 6.4%.
Thanks to its unique energy distribution network, the company has a strong competitive position. Set against that is the fact that its pricing is subject to regulatory constraints.
Share price volatility
No share is ever an assured safe haven, though, no matter how resilient the business may seem. National Grid shares have moved up 17% over the past five years. But within that period there has been a lot of up and down.
Within a few months in 2022, for example, the shares dropped almost 30%. A recent rights issue to raise more cash for the utility has also seen the share price tumble 14% in little over a month.
What about the dividend?
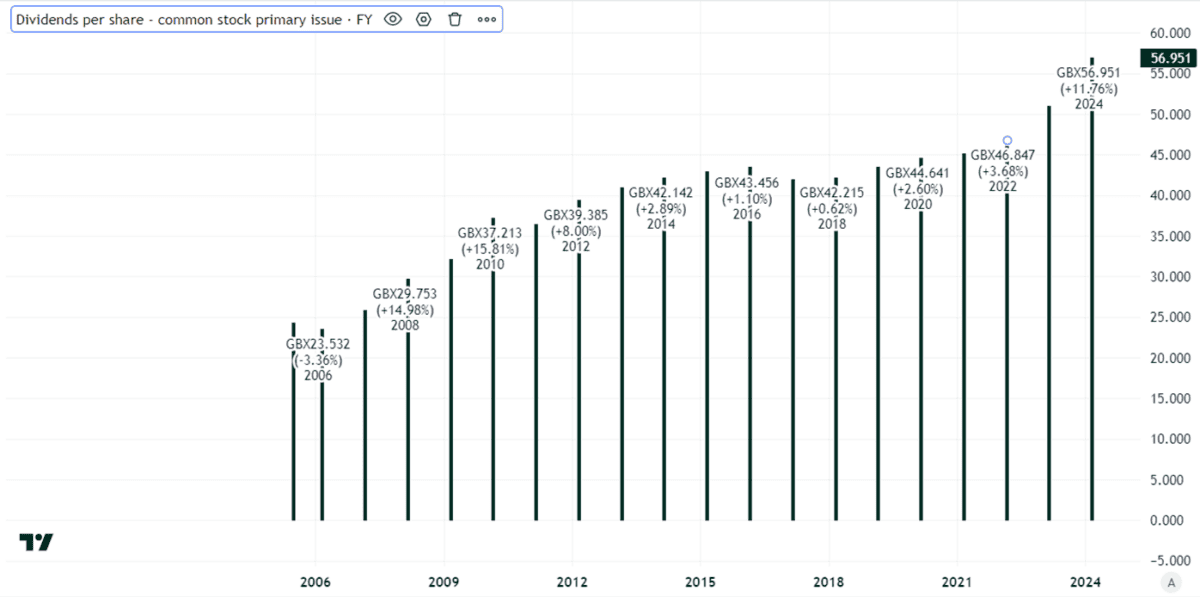
History of dividend rises
The National Grid dividend per share has risen steadily over many years.
Created using TradingView
The payout per share has doubled. But that has been a long process, stretching over 17 years.
On the one hand this might seem like slow progress. Yes, I am a long-term investor, but inflation over that period has been around 64%, so in real terms the gain per year has been fairly modest (though still a gain).
But is this not exactly the appeal of utility shares? During the past 17 years, many shares have cut or cancelled their dividends. The National Grid dividend has actually grown in real value even after considering the impact of inflation.
Can it keep increasing?
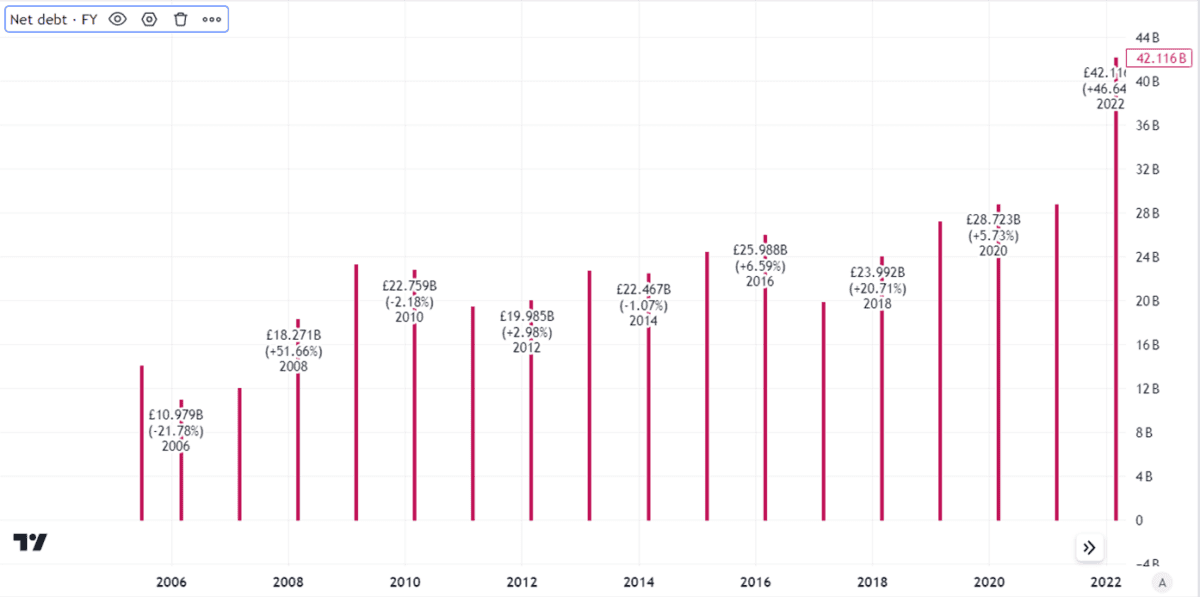
Past performance is not necessarily a guide to what will happen in future, though. This is a company that has high capital expenditure requirements, due to the costly nature of building and maintaining power transmission infrastructure.
In recent years that has placed an increasingly heavy strain on the firm’s balance sheet. Net debt is substantial.
Created using TradingView
That debt load helps explain the recent rights issue. But in the long term, I think it poses a risk to the dividend. After all, servicing debt eats into a company’s free cash flows.
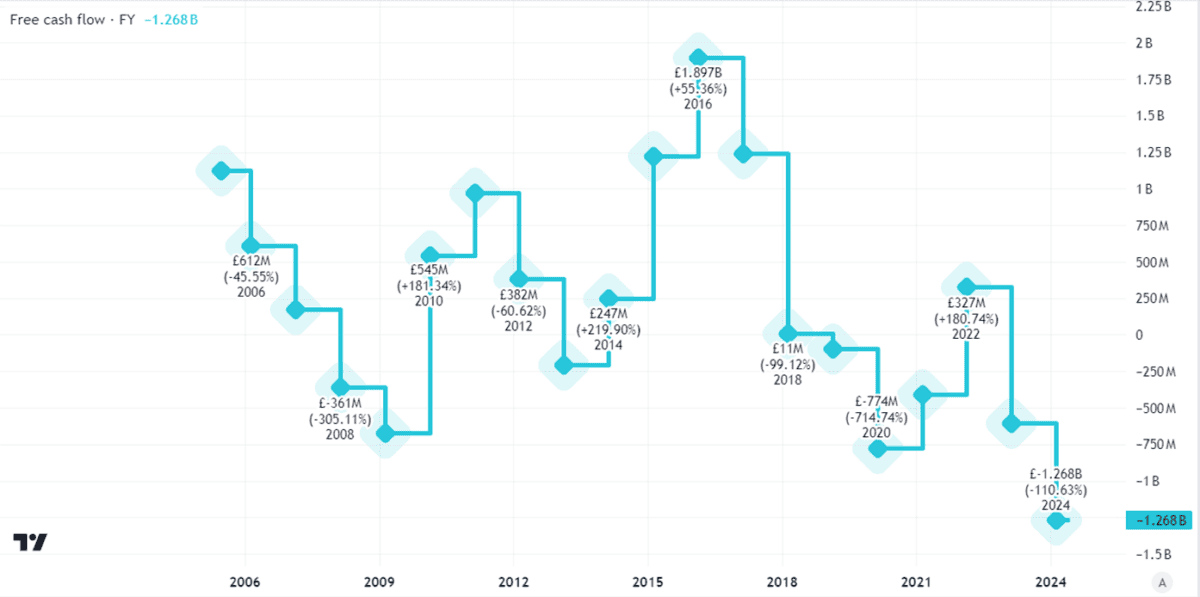
I do not like the look of National Grid’s free cash flows.
Created using TradingView
Dividends are included in those cash flows. So if a company wants to improve its free cash flows, some options open to it are raising more cash (as National Grid has recently done) or cutting the dividend. Holding the dividend flat instead of increasing it could also help free cash flows.
With its high ongoing capital expenditure requirements and sizeable debt, I think it could take decades for the National Grid dividend to double again – if it ever does. I am more concerned about the risk of a dividend cut during that period. I have no plans to invest.
This post was originally published on Motley Fool